概念
反射是 Java 的特征之一,是一种简介操作目标对象的机制,其核心是 JVM 在运行状态时才动态地加载类(任意一个类都能够知道这个类所有的属性和方法,并且都能够调用这个类的方法和访问属性)。这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能成为 Java 的反射机制。
作用
在程序运行前,不需要知道运行的对象是谁,在程序运行时,获得每一个类型的成员和成员的信息,达到动态创建、修改、调用、获取其属性的目的(在运行时而不是编译时,不改变原有代码逻辑,自行运行时动态创建和编译)
流程图
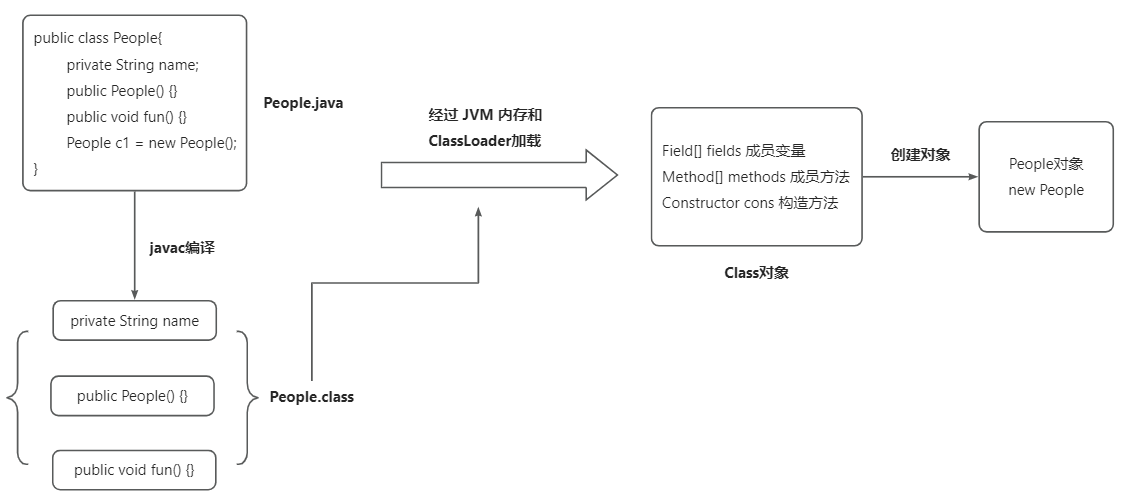
使用场景
构造利用链,触发命令执行
反序列化的利用链构造
动态地获取或执行任意类当中的属性或方法
rmi反序列化
动态代理的底层原理也用到了反射技术
方法
以 User 类为例(在每个软件包中创建这个类)
public class User {
public String Name;
public String Sex;
private int Age;
protected String Address;
public User() {}
public User(String name, String sex){
Name = name;
Sex = sex;
}
private User(String name, String sex, int age){
Name = name;
Sex = sex;
}
protected User(String name, String sex, int age, String address){
Name = name;
Sex = sex;
Age = age;
Address = address;
}
private void Say(String Job, int PhoneNumber) {
System.out.println("My name is " + Name);
System.out.println("My age is " + Age);
System.out.println("My Job is " + Job);
System.out.println("My PhoneNumber is " + PhoneNumber);
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return Sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
Sex = sex;
}
private int getAge() {
return Age;
}
private void setAge(int age) {
Age = age;
}
protected String getAddress() {
return Address;
}
protected void setAddress(String address) {
Address = address;
}
}Class对象类获取
package com.example.Class;
public class ClassGetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
User u = new User();
// -------------------------------class--------------------------------
Class<User> GClass = User.class;
System.out.println(GClass);
// 输出 class com.example.Class.User
// -----------------------------getClass()-----------------------------
Class<? extends User> getClass = u.getClass();
System.out.println(getClass);
// 输出 class com.example.Class.User
// ----------------------forName(String className)----------------------
Class<?> forName = Class.forName("com.example.Class.User");
System.out.println(forName);
// 输出 class com.example.Class.User
// -----------getSystemClassLoader() 和 loadClass(String name)-----------
ClassLoader SystemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(); // 创建系统类加载器
Class<?> loadClass = SystemClassLoader.loadClass("com.example.Class.User"); // 使用系统类加载器获取对象类
System.out.println(SystemClassLoader);
System.out.println(loadClass);
// 输出
// jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@36baf30c
// class com.example.Class.User
}
}
Field成员变量类获取
package com.example.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class FieldGetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> GClass = Class.forName("com.example.Field.User");
// --------------------------------getFields()--------------------------------
Field[] Fields = GClass.getFields();
for (Field f:Fields) {
System.out.println(f);
// 输出
// public java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Name
// public java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Sex
}
// ----------------------------getDeclaredFields()----------------------------
Field[] DeclaredFields = GClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f:DeclaredFields) {
System.out.println(f);
// 输出
// public java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Name
// public java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Sex
// private int com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Age
// protected java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Address
}
// ---------------------------getField(String name)---------------------------
Field Field1 = GClass.getField("Name");
System.out.println(Field1);
// 输出 public java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Name
// -----------------------getDeclaredField(String name)-----------------------
Field Field2 = GClass.getDeclaredField("Age");
System.out.println(Field2);
Field Field3 = GClass.getDeclaredField("Address");
System.out.println(Field3);
// 输出
// private int com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Age
// protected java.lang.String com.example.FieldGetTest.User.Address
// --------------set(Object obj, Object value) 和 get(Object obj)---------------
User u = new User();
Field field = GClass.getField("Name"); // 获取 User 类中的 Name 属性
field.set(u, "Xao"); // u 的 Name 属性赋值为 Xao
Object a = field.get(u); // 获取对象 u 的 Name 属性
System.out.println(a);
// 输出 Xao
}
}
Method成员方法类获取
package com.example.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MethodGetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> GClass = Class.forName("com.example.Method.User");
// ---------------------------getMethods()---------------------------
Method[] Methods = GClass.getMethods();
for (Method m:Methods){
System.out.println(m);
// 输出
// public java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getSex()
// public void com.example.Method.User.setSex(java.lang.String)
// public java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getName()
// public void com.example.Method.User.setName(java.lang.String)
// public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
// public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()
// public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
// public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
// public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
// public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
// public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
// public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
// public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
}
// -----------------------getDeclaredMethods()-----------------------
Method[] DeclaredMethods = GClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m:DeclaredMethods) {
System.out.println(m);
// 输出
// public java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getName()
// public void com.example.Method.User.setName(java.lang.String)
// protected java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getAddress()
// private void com.example.Method.User.setAge(int)
// public java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getSex()
// private void com.example.Method.User.Say(java.lang.String,int)
// private int com.example.Method.User.getAge()
// public void com.example.Method.User.setSex(java.lang.String)
// protected void com.example.Method.User.setAddress(java.lang.String)
}
// ----------------------------getMethod()----------------------------
Method method1 = GClass.getMethod("getName");
System.out.println(method1);
Method method2 = GClass.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(method2);
// 输出
// public java.lang.String com.example.Method.User.getName()
// public void com.example.Method.User.setName(java.lang.String)
// ------------------------getDeclaredMethod()------------------------
Method DeclaredMethod = GClass.getDeclaredMethod("Say", String.class, int.class);
System.out.println(DeclaredMethod);
// 输出 private void com.example.Method.User.Say(java.lang.String,int)
// -----------------------------invoke()------------------------------
Method InvokeMethod = GClass.getDeclaredMethod("Say", String.class, int.class);
User u = new User(); // 创建一个新对象
InvokeMethod.setAccessible(true); // 私有方法开启临时,其他不需要
InvokeMethod.invoke(u, "Teacher", 10010); // 执行 Say 私有方法,传入参数 Teacher(String) 10010(int)
// 运行结果
// My name is null
// My age is 0
// My Job is Teacher
// My Number is 10010
}
}
Constructor构造方法类获取
package com.example.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class ConstructorGetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> GClass = Class.forName("com.example.Constructor.User");
// ------------------------getConstructors()------------------------
Constructor[] Constructors = GClass.getConstructors();
for (Constructor c:Constructors) {
System.out.println(c);
// 输出 public com.example.Constructor.User()
}
// --------------------getDeclaredConstructors()--------------------
Constructor[] DeclaredConstructors = GClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c:DeclaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(c);
// 输出
// public com.example.Constructor.User()
// protected com.example.Constructor.User(java.lang.String,java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
// private com.example.Constructor.User(java.lang.String,java.lang.String)
}
// -------------------------getConstructor()-------------------------
Constructor con1 = GClass.getConstructor();
System.out.println(con1);
Constructor con2 = GClass.getConstructor(String.class, String.class);
System.out.println(con2);
// 输出
// public com.example.Constructor.User()
// public com.example.Constructor.User(java.lang.String,java.lang.String)
// ---------------------getDeclaredConstructor()---------------------
Constructor con3 = GClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
System.out.println(con3);
Constructor con4 = GClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, int.class);
System.out.println(con4);
// 输出
// public com.example.Constructor.User()
// private com.example.Constructor.User(java.lang.String,java.lang.String,int)
// ---------------------------newInstance()---------------------------
con4.setAccessible(true);
User u = (User) con4.newInstance("Xao", "Male", 20); // 运行结果如下
System.out.println(u); // com.example.Constructor.User@433c675d
System.out.println(u.Name); // Xao
System.out.println(u.Sex); // Male
System.out.println(u.Address); // null
// Address属性为protected,所以不输出,Age为私有属性,无法直接获取
}
}
不安全命令执行与反序列化链条
以 Runtime.getRuntime().exec("notepad"); 为例,用上述方法来反射这个对象。截取 Runtime 类中部分方法
public class Runtime {
private static java.lang.Runtime currentRuntime = new java.lang.Runtime();
public Process exec(String command) throws IOException {
return exec(command, null, null);
}
public static Runtime getRuntime() {
return currentRuntime;
}
}可见,getRuntime() 方法是用于返回一个 Runtime 类对象,再通过这个类对象调用 exec() 方法,来执行命令。
首先要获取 Runtime 类
Class<?> c = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");接下来有两种方法获取 Runtime 类对象
使用 Runtime 类中的方法
getRuntime()获取 Runtime 类对象
Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime");
Object Run = getRuntime.invoke(c);使用 Runtime 类构造方法创建 Runtime 类对象
Constructor Runtime = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
Runtime.setAccessible(true); // 私有方法需要设置
Object Run = Runtime.newInstance();获取并调用 Runtime 对象中的 exec() 方法,执行命令 "notepad"
Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
exec.invoke(Run,"notepad");最后弹出记事本,完成命令执行。


参与讨论